Enlarged Prostate Treatments
 How an enlarged prostate is treated depends greatly on how severe the symptoms are, how much they are affecting your everyday life, and if other medical issues are present. There are many remedies available, which include just keeping an eye on the symptoms, changing your lifestyle in small ways, taking prescription medications, or undergoing a surgical procedure.
How an enlarged prostate is treated depends greatly on how severe the symptoms are, how much they are affecting your everyday life, and if other medical issues are present. There are many remedies available, which include just keeping an eye on the symptoms, changing your lifestyle in small ways, taking prescription medications, or undergoing a surgical procedure.
You are more apt to experience symptoms if you are 60 years of age or older. However, a great number of guys who have enlarged prostates do not experience severe symptoms. In these cases, most men can simply make some minor lifestyle changes to relieve the symptoms.
If you do have an enlarged prostate that has been diagnosed as BPH, you will want to be seen by a physician on a yearly basis to make sure it is not getting any worse. If it is, the treatment can be altered to fit your needs.
Lifestyle Changes for Mild Symptoms
1. If you feel like you need to urinate, do it immediately. In addition, take the opportunity to go to urinate even if the urge is not there.
2. Do not drink caffeinated beverages or coffee, particularly at night.
3. Drink fluids all day long instead of all at once. Do not drink anything in the two hours before going to bed.
4. If you can help it, avoid taking non-prescription cold or sinus drugs that include antihistamines or decongestants. These ingredients make BPH symptoms worse.
5. Do not allow yourself to get cold and get adequate exercise. BPH symptoms are often exacerbated from the cold and from not working out enough.
6. Strengthen your pelvic region by performing Kegal exercises.
7. Lower your stress level since anxiety and pressure can trigger the need to urinate more often.
Drugs
1. A kind of medication that can remedy hypertension can also help relieve the tension in the prostate and bladder neck muscles. These are called Alpha 1-blockers and include alfuzosin, terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and prazoxin. When these muscles are relaxed, urination becomes easier. This is usually a very effective treatment.
2. To reduce the amount of hormones that the prostate makes, to shrink the prostate, to improve the flow of urine, and to generally lessen BPH symptoms, doctors often prescribe dutasteride or finasteride. The effects of these medications are not instant and may require up to 6 months of use before you see a reduction in your symptoms. These drugs can also lower the sex drive and cause impotency.
3. If chronic prostatitis is present, which is the swelling of the prostate, antibiotics are often used to treat this inflammation.
4. A natural medication that is often used to treat BPH is saw palmetto. It is many times suggested as an option that doesn’t involve synthetic medications. Even though many men swear that it is effective, there is the idea that it does not work any better than taking nothing at all. If you have been taking saw palmetto and believe it has been effective in your situation, you should speak with a physician to see if it is still safe for you to take.
Surgical Procedures
Undergoing surgery is only usually necessary if you suffer from:
1. Incontinence
2. Blood in your urine that never gets better
3. Inability to completely void your bladder, which is also called urinary retention
4. Chronic urinary tract infections
5. A decrease in kidney function
6. Stones in the bladder
What kind of surgical procedure you undergo depends on your symptoms and how large your prostate gland is.
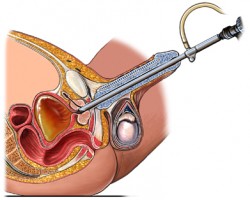
1. TURP or transurethral resection of the prostate. This procedure involves putting a scope into the urethra and taking out parts of the prostate. This is the most prevalent and effective surgical solution to BPH.
2. TUIP or transurethral incision. This surgical treatment is reserved for men with smaller prostates, but it is very similar to TURP. It is typically performed on an out-patient basis. As with TURP, a scope is put into the urethra and directed to the prostate. A tiny cut is made to the prostate which allows for the enlargement of the hole that accesses the bladder and urethra. Unlike with TURP, no part of the prostate is removed.
3. Simple Prostatectomy. This procedure is typically performed on an inpatient basis. The patient will be required to stay in the hospital for as many as 10 days. A cut is made into the stomach area behind the scrotum and the inside portion of the prostate is taken out. General or spinal anesthesia is typically required.
The majority of guys who undergo one of the above surgical procedures indicate that their symptoms are alleviated and their flow of urine increases.
Less-Invasive Surgical Procedures
For those of you who would rather undergo a less-invasive procedure, there are several techniques available that use heat to kill the prostate tissue. These are:
1. TUNA or transurethral needle ablation which uses radio waves to create the heat
2. TUMT or transurethral microwave thermotherapy which uses microwaves to create the heat
3. TUVP or transurethral electrovaporization which uses electricity to create the heat
4. WIT or water-induced thermotherapy which uses hot water to create the heat
5. ILC or interstitial laser coagulation and HoLEP or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate which use lasers to create the heat
While these procedures are generally effective, none of them have been able to equal the effectiveness of TURP. Men who undergo the less-invasive procedures will usually have to repeat the procedure again in 5-to-10 years. Even so, the less-invasive options would be best for:
1. Men who are younger
2. Men who are quite a bit older
3. Men who have other medical problems like cirrhosis, diabetes, psychosis, alcoholism, and severe heart, lung, or kidney disease
4. Men who are on drugs designed to thin the blood.
A newer method, known as robot-guided prostatectomy has been recently introduced. But this procedure is not yet available everywhere, and even if it is, the experience of the surgeon may not be on par with other procedures. Moreover, long-term results of this procedure are not yet known.